Issue
In a performance testing, the Linux system is not in high loads (40% of total CPUs is in use), but our service can’t receive more requests and the ssh connections frequently disconnected.
Investigation
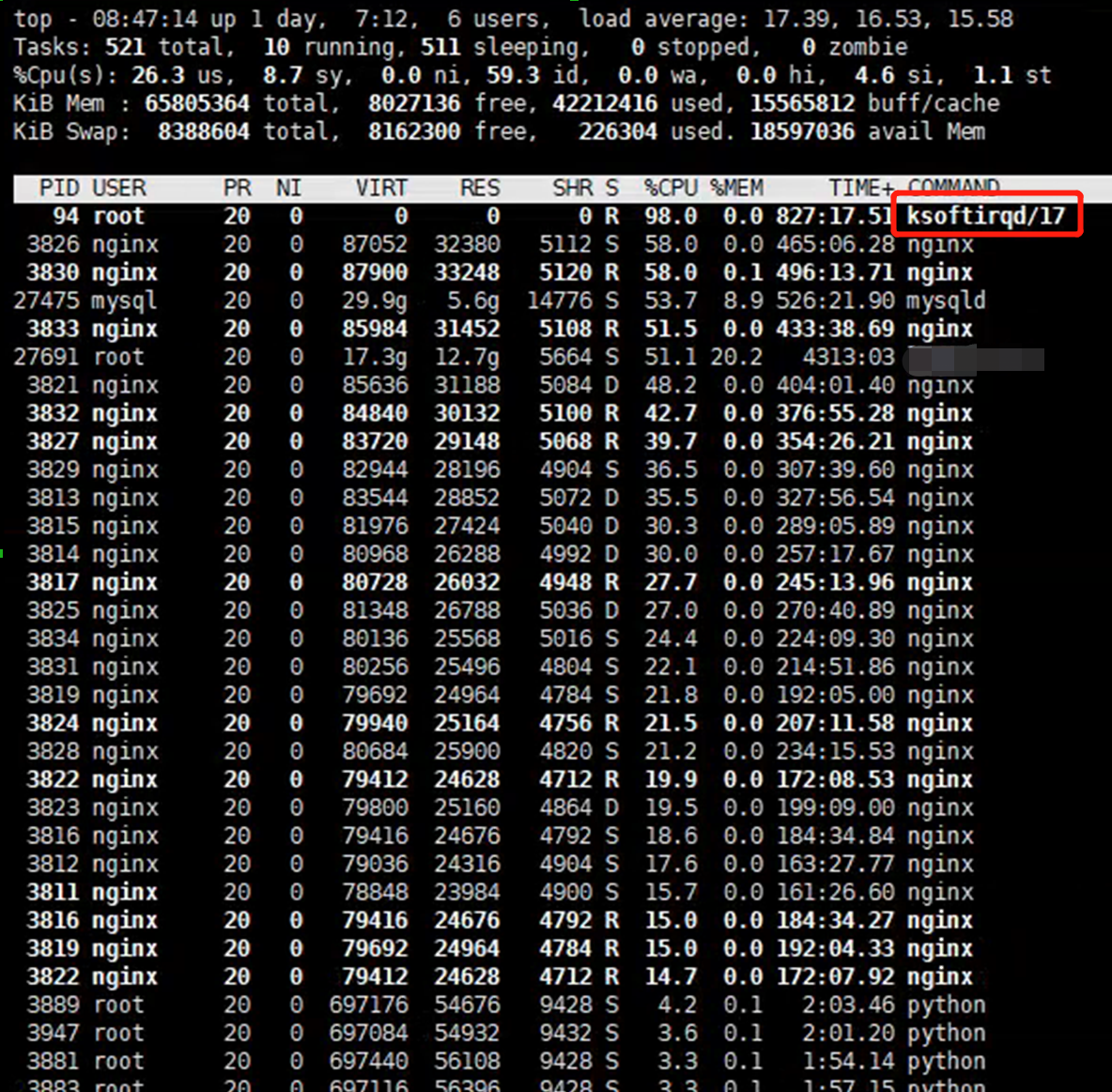
The testing environment was built on a KVM, and it was assigned 24 CPU cores. In top output, ksoftirqd/17 occupied 98% CPU. ksoftirqd is used to handle the interrupt from hardware, so maybe this process is the bottleneck of the system.
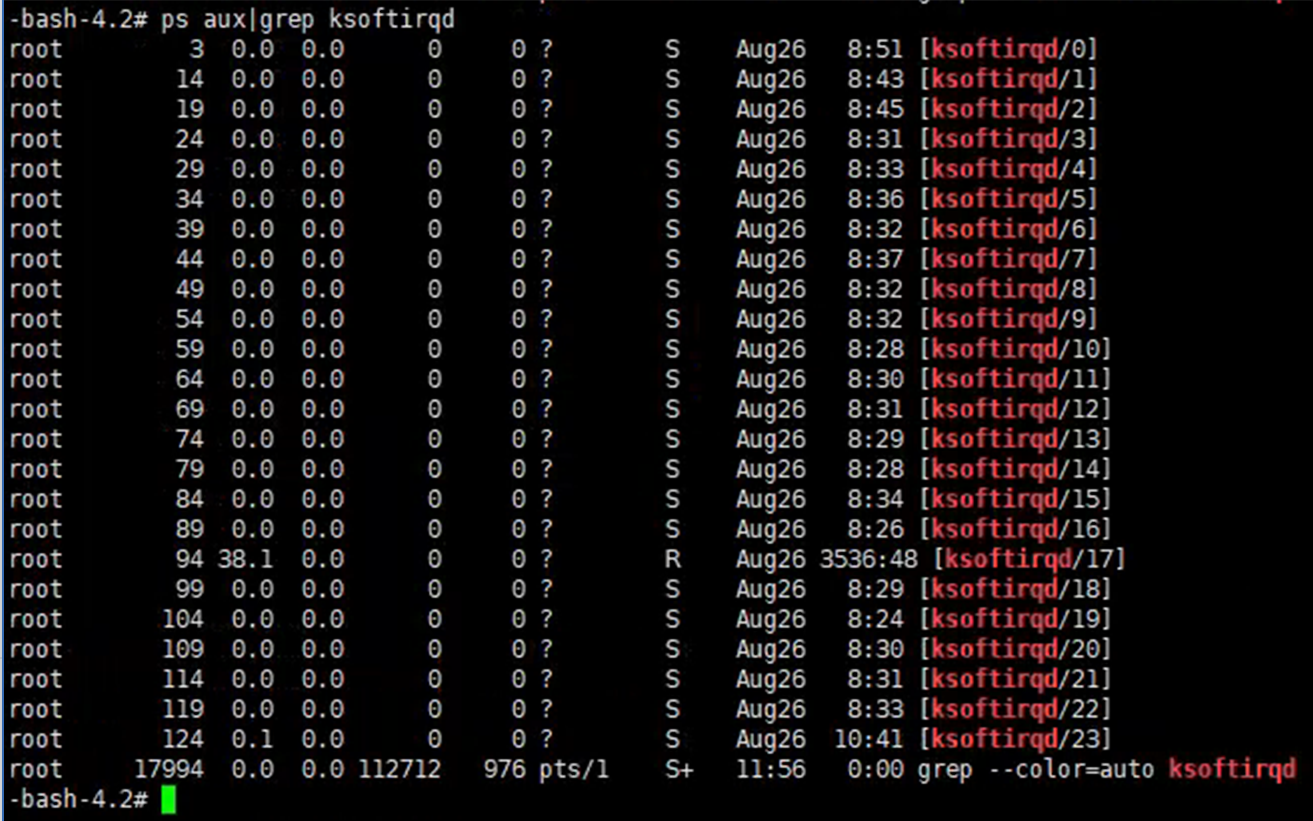
There are 24 ksoftirqd processes related to 24 CPU cores, but only ksoftirqd/17 is very busy. So let’s check what ksoftirqd/17 is working for. /proc/interrupts recorded the interrupt information. Our NIC is ens3. We can see int 11 is working for ens3, and a large number of int 11 occured in CPU17, which is related with ksoftirqd/17.
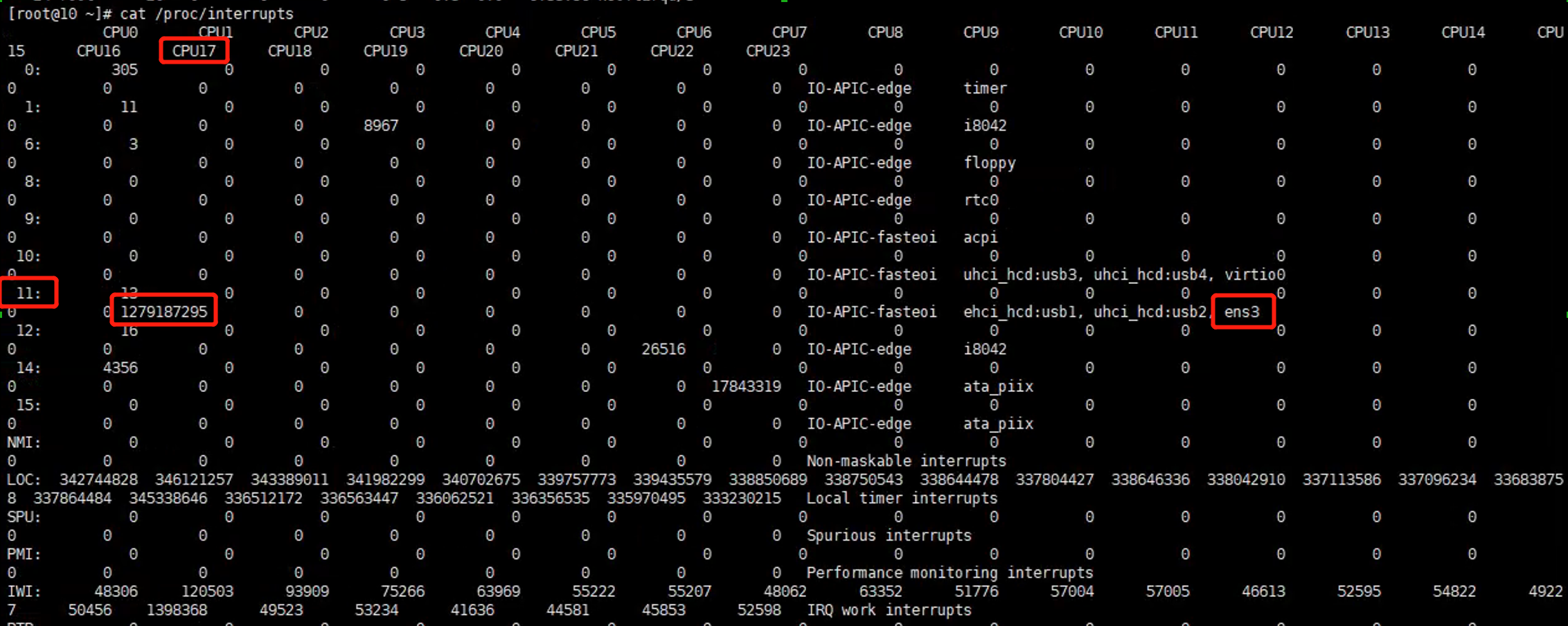
Obviously the NIC interrupts are not distributed to multiple CPUs. All NIC interrupts are only sent to ksoftirqd/17, and cause CPU 17 is too busy to process more packets.
The other CPUs are not fully utilized, so we need to distribute the NIC interrupts to other CPUs to improve the system performance.
Solve it
Run ethtool -l ens3 to query NIC channels:
1
2
3
4
# ethtool -l ens3
Channel parameters for ens3:
Cannot get device channel parameters
: Operation not supported
It looks the driver of NIC didn’t support multiple channels. Otherwise, we can use ethtool -L ens3 combined 8 to change channels, which means 8 cpu could handle soft irq.
Irqbalance service is running, but it seems irqbalance can’t handle this case. We need to distribute the NIC interrupts manually by using Receive Packet Steering(RPS) and Receive Flow Steering(RFS).
RPS works in Linux kernel to distribute NIC interrupts to multiple CPUs. RFS is to increase datacache hitrate by steering kernel processing of packets to the CPU where the application thread consuming the packet is running. The full document about network scaling could found at https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/scaling.txt.
Just list the steps I did:
- Disable irqbalance service.
1
2
# systemctl stop irqbalance
# systemctl disable irqbalance
- Set SMP IRQ affinity. We could assign which CPUs can process the specific interrupt. In this VM, int 11 works for NIC interrupts, and I want all CPU cores could process the NIC interrupts.
1
# echo "0-23" > /proc/irq/11/smp_affinity_list
- Alternatively, you could set the smp_affinity by hex value. We can check the last command by
cat /proc/irq/11/smp_affinity, and get “ffffff”.
- Configure RPS. “ffffff” is a bitmap of CPUs.
1
# echo "ffffff" > /sys/class/net/ens3/queues/rx-0/rps_cpus
- Configure RFS. For a single queue device, we set rps_sock_flow_entries and rps_flow_cnt value with the same value for a good performance.
1
2
# sysctl -w net.core.rps_sock_flow_entries=32768
# echo 32768 > /sys/class/net/ens3/queues/rx-0/rps_flow_cnt
All done
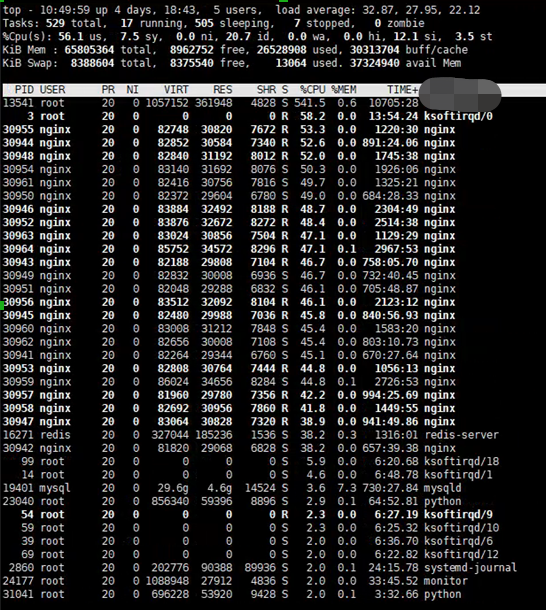
The NIC interrupts are distributed to multiple CPU cores, so our backend service can handle more requests and the whole system is fully utilized.
Comments powered by Disqus.